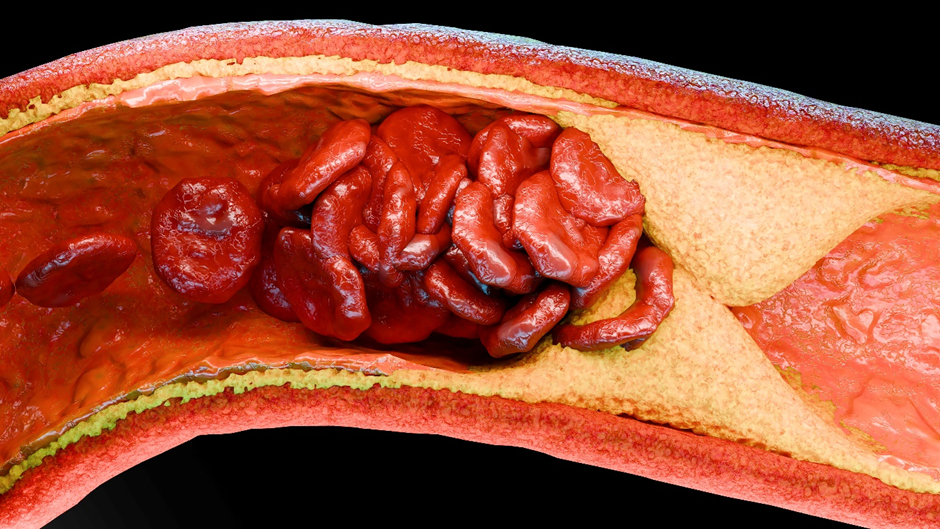
High cholesterol, or hyperlipidemia, is a common condition that increases the risk of heart disease and strokes.
Understanding Hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia means having too many lipids (fats) in your blood.
This condition is primarily concerned with high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), known as “bad” cholesterol, and very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), which carries triglycerides.
High levels of these lipids lead to the buildup of plaque in your arteries, narrowing and hardening them, which impedes blood flow and can lead to heart attacks or strokes.
High-density lipoprotein (HDL), or “good” cholesterol, helps remove other forms of cholesterol from your bloodstream.
Unlike LDL and VLDL, higher levels of HDL are beneficial and can protect against heart attack and stroke.
Causes and Risk Factors
The main cause of high cholesterol can be genetic or lifestyle-related.
Factors that can increase your risk include poor diet, physical inactivity, smoking, excessive alcohol use, obesity, and conditions like diabetes, hypothyroidism, and liver or kidney disease.
Some medications can also raise cholesterol levels, including certain birth controls, diuretics, and steroids.
Genetics also play a significant role.
Familial hypercholesterolemia is an inherited form of high cholesterol that can lead to early heart disease.
Moreover, if high cholesterol runs in your family, you may be more likely to develop it as well.
Diagnosis and Testing
Hyperlipidemia is diagnosed through a lipid panel, a blood test that measures total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. Ideal levels are:
- Total cholesterol: less than 200 mg/dL
- LDL cholesterol: less than 100 mg/dL
- HDL cholesterol: 60 mg/dL or higher
- Triglycerides: less than 150 mg/dL
This condition is particularly dangerous because it typically does not cause any symptoms until serious damage has occurred.
As such, regular screening is critical, especially if you have risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Treatment and Management
Treatment for hyperlipidemia includes lifestyle changes and, if necessary, medications. Key lifestyle modifications include:
- Switch to a heart-friendly diet that includes abundance of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, and minimizes saturated and trans fats. Also, aim to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week.
- Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake.
- Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
When lifestyle changes are not enough to reduce cholesterol levels, medications may be prescribed. Statins are the most common medication for lowering LDL levels and reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Other medications may include cholesterol absorption inhibitors, bile acid sequestrants, and injectable medications that help the liver absorb more LDL cholesterol.
Prevention and Long-Term Outlook
Managing hyperlipidemia effectively requires the same preventive measures: eating a nutritious diet, exercising regularly, avoiding smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight. Consistent cholesterol monitoring is crucial for early detection and more effective treatment.
For those diagnosed with hyperlipidemia, it’s essential to continuously manage the condition to prevent heart disease. This involves sticking to prescribed treatments, attending regular check-ups to track cholesterol levels, and adjusting treatments as necessary.
Dealing with high cholesterol demands a lifelong commitment to maintaining heart health. Through diligent management, people with hyperlipidemia can enjoy long and healthy lives. It is important to collaborate closely with healthcare providers to customize a treatment plan that suits your specific needs and lifestyle.
Conclusion
If you suspect you have high cholesterol or if it runs in your family, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider to get a lipid panel test.
Don’t wait for symptoms to appear, as high cholesterol does not typically cause any until it’s already a severe problem.
Take control of your health by making lifestyle changes and following medical advice to manage or prevent high cholesterol. Remember, the power to protect your heart is in your hands.
This comprehensive approach to understanding, diagnosing, and managing hyperlipidemia underscores the importance of proactive healthcare and lifestyle choices in maintaining heart health and preventing serious complications. By staying informed and vigilant, you can significantly improve your quality of life and longevity.