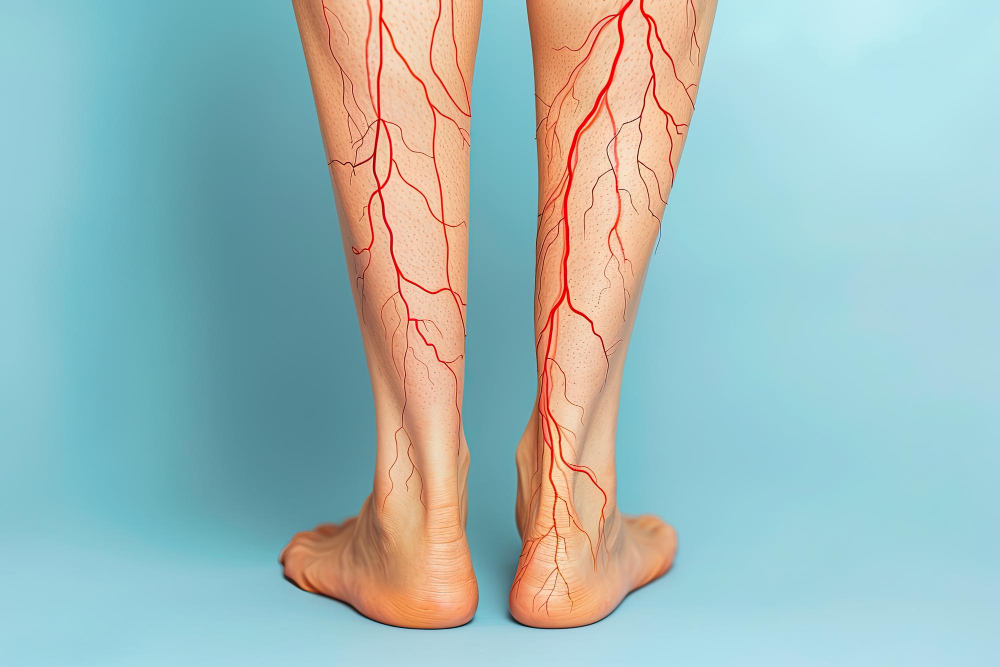
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the leg. DVT is important in cardiology because these clots can block blood flow and may travel to the lungs, causing a life-threatening problem called pulmonary embolism. Both non-interventional and interventional cardiologists help manage DVT to protect your heart and blood vessels. Knowing about DVT, its symptoms, and how to prevent it can help you stay healthy and safe.
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Deep Vein Thrombosis means a blood clot forms in a deep vein, often in the lower leg or thigh. These veins carry blood from your legs back to your heart. When a clot blocks the flow, it can cause pain and swelling. Sometimes, the clot can break loose and travel to your lungs. This is called a pulmonary embolism, which is a medical emergency. DVT is a type of blood clot problem that cardiologists often treat. It can happen to anyone, but some people are at higher risk.
Common Symptoms of DVT
Recognizing DVT symptoms early is important. However, some people may not notice any signs. Still, you should watch for these common symptoms:
Sometimes, DVT can cause no symptoms at all. But if you notice sudden swelling or pain, you should seek medical help right away. Early treatment can prevent serious problems.
Causes and Risk Factors
Many things can cause DVT. Some people have a higher risk because of their health or lifestyle. Here are some common causes and risk factors:
Because these factors can increase your risk, it is important to talk to your doctor if you have any concerns. According to the CDC, about 900,000 people in the United States may be affected by DVT each year.
How DVT is Diagnosed
Doctors use several methods to diagnose DVT. First, they will ask about your symptoms and medical history. Then, they may do a physical exam. If DVT is suspected, your doctor may order tests such as:
Early diagnosis helps prevent complications. If you have symptoms, do not wait to get checked.
Treatment Options for DVT
Treating DVT aims to stop the clot from growing and prevent it from moving to the lungs. Common treatment options include:
Your doctor will choose the best treatment based on your health and risk factors. Always follow your doctor’s advice and take medicines as prescribed.
Prevention Tips and Lifestyle Guidance
Preventing deep vein thrombosis is possible with some healthy habits. Here are some tips to lower your risk:
Because prevention is better than cure, making small changes can protect your health. The World Health Organization and CDC both recommend staying active and managing risk factors to prevent DVT.
When to Seek Medical Help
If you notice sudden swelling, pain, or redness in your leg, seek medical help right away. Also, if you have trouble breathing, chest pain, or cough up blood, call emergency services. These may be signs of a pulmonary embolism, which needs urgent care. Early treatment can save lives and prevent serious problems.
For more information or if you have concerns about DVT, consult a healthcare specialist for personalized advice on Deep Vein Thrombosis.